Understanding The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) And Its Role In Shaping The Economy
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is a cornerstone of the U.S. economic framework, influencing monetary policy and fostering economic stability. As part of the Federal Reserve System, the FOMC plays a central role in making decisions that impact interest rates, employment, and inflation. Whether you're an economics enthusiast, a seasoned investor, or simply curious about how monetary policy affects daily life, understanding the FOMC is crucial.
The FOMC's decisions reverberate across both domestic and international financial landscapes. By setting monetary policy, the committee directly influences key economic indicators such as inflation, employment levels, and overall growth. These actions also affect stock markets, bond yields, and currency values, making the FOMC a critical focus for investors and policymakers alike. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the FOMC's functions, responsibilities, and the broader implications of its decisions.
In this detailed exploration, we will examine the inner workings of the FOMC, its responsibilities, and how its actions shape the economy. Whether you're a student, investor, or someone interested in understanding how monetary policy impacts your financial well-being, this article will offer valuable insights into the significance of the FOMC.
Read also:Exploring The Essence Of American Identity And Culture
Table of Contents
- What is the FOMC?
- FOMC Members and Structure
- Monetary Policy and the FOMC
- FOMC Meetings and Their Importance
- Understanding FOMC Statements
- The Impact of FOMC Decisions on the Economy
- How Investors Interpret FOMC Decisions
- A Historical Perspective on the FOMC
- Challenges Faced by the FOMC
- Conclusion and Next Steps
An Introduction to the Federal Open Market Committee
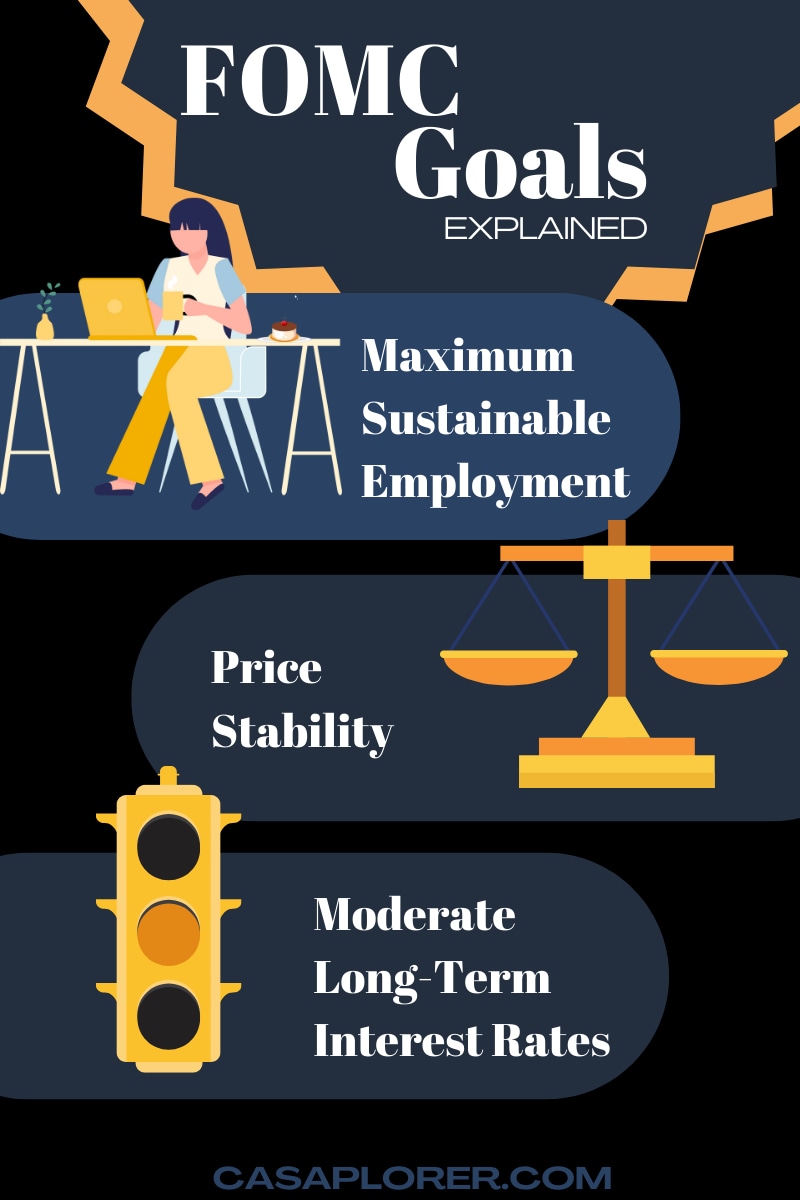
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) serves as the monetary policymaking body of the Federal Reserve System. Established in 1913 under the Federal Reserve Act, the FOMC is tasked with implementing monetary policy to achieve key economic objectives, including maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates. The committee achieves these goals through open market operations, setting target federal funds rates, and adjusting reserve requirements.
Operating under the Federal Reserve, the central banking system of the United States, the FOMC plays a pivotal role in ensuring economic stability and growth. By managing monetary policy, the committee addresses inflationary pressures, unemployment, and fosters an environment conducive to sustainable economic development.
The Core Objectives and Mission of the FOMC
The primary goals of the FOMC, as outlined in the Federal Reserve Act, are:
- Maximizing Employment: Ensuring the economy operates at its full potential by reducing unemployment rates and supporting workforce participation.
- Stabilizing Prices: Controlling inflation to preserve purchasing power and maintain economic stability.
- Promoting Moderate Long-Term Interest Rates: Encouraging sustainable economic growth by balancing borrowing costs for consumers and businesses.
These objectives, collectively known as the "dual mandate," emphasize the committee's commitment to fostering both employment and price stability, making it a cornerstone of U.S. economic policy.
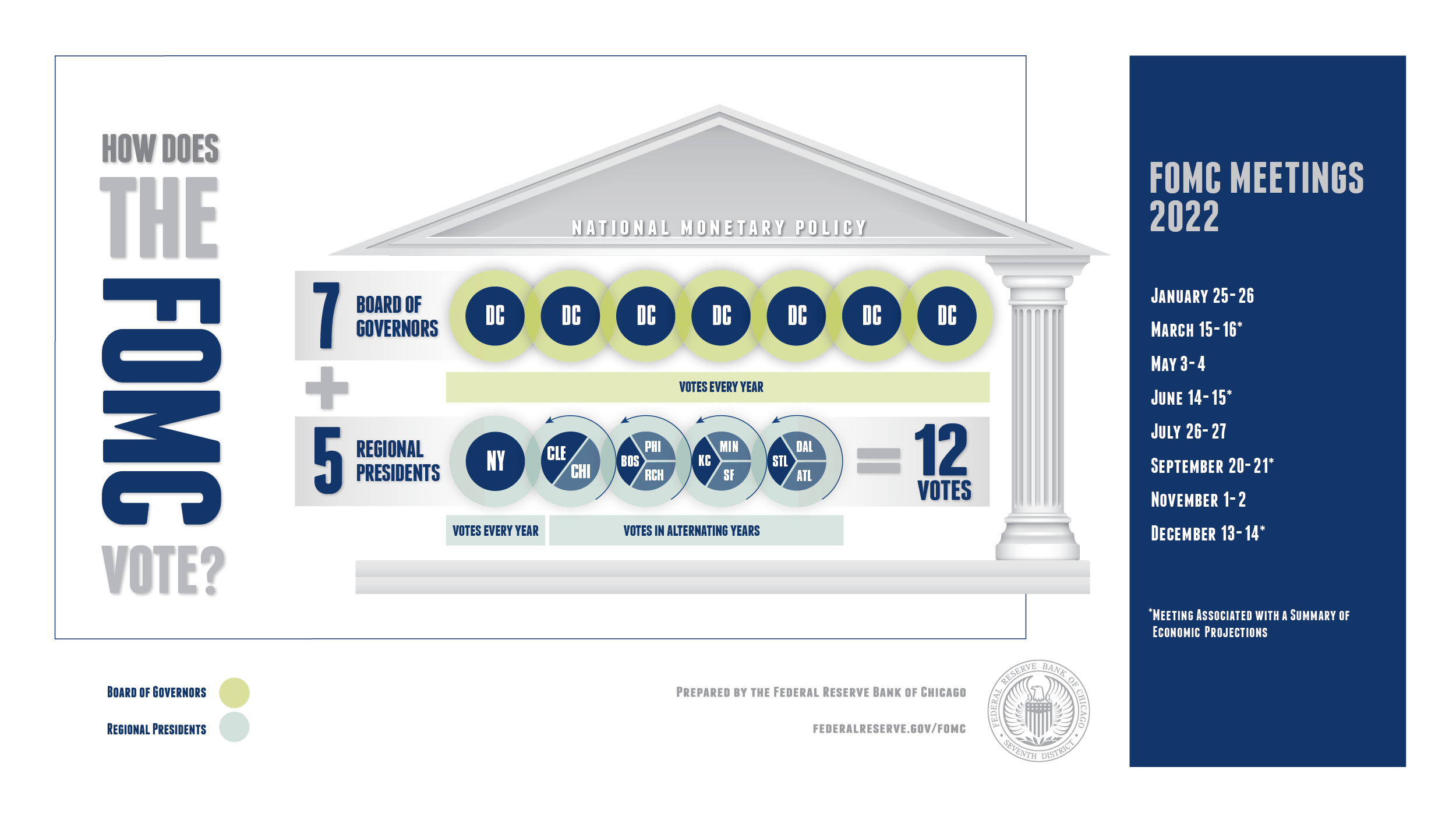
The Composition and Structure of the FOMC
The FOMC is composed of 12 members, including the seven members of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System and five of the 12 Federal Reserve Bank presidents. The President of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York holds a permanent voting position, while the remaining four voting slots rotate annually among the other Reserve Bank presidents.
The Role and Responsibilities of FOMC Members
The structure of the FOMC is designed to balance centralized authority with regional representation, ensuring decisions reflect diverse economic perspectives. Key roles within the committee include:
Read also:Mt St Marys Basketball A Legacy Of Excellence And Community
- Chair of the Federal Reserve: The Chair leads the FOMC and plays a critical role in shaping monetary policy decisions, providing guidance and direction to the committee.
- Vice Chair: Assisting the Chair, the Vice Chair supports the decision-making process and ensures smooth operations during FOMC meetings.
- Regional Reserve Bank Presidents: Offering insights into local economic conditions, these members ensure that regional perspectives are integrated into policy decisions.
This diverse composition enables the FOMC to make informed decisions that align with the broader economic realities of the United States.
Monetary Policy: The FOMC's Tools for Economic Stability
Monetary policy encompasses the actions taken by the FOMC to influence the availability and cost of money and credit in the economy. To achieve its objectives, the FOMC employs three primary tools:
- Open Market Operations: The buying and selling of government securities to influence the federal funds rate and control the money supply.
- Federal Funds Rate: Setting a target range for the interest rate at which banks lend reserve balances to each other overnight, impacting borrowing costs for consumers and businesses.
- Reserve Requirements: Adjusting the amount of reserves banks must hold against deposits to influence the level of credit available in the economy.
Through the strategic use of these tools, the FOMC can effectively manage economic activity, inflation, and employment levels.
A Closer Look at the Tools of Monetary Policy
Each tool utilized by the FOMC serves a unique purpose in shaping economic conditions:
- Open Market Operations: When the FOMC purchases securities, it injects money into the economy, lowering interest rates and stimulating growth. Conversely, selling securities reduces the money supply, raising interest rates and slowing economic activity.
- Federal Funds Rate: This rate directly influences borrowing costs, affecting consumer spending and business investment decisions. Adjustments to the federal funds rate are a key mechanism for controlling inflation and supporting economic stability.
- Reserve Requirements: By modifying reserve requirements, the FOMC can control the amount of credit available in the economy, influencing lending practices and economic activity.
These tools are carefully calibrated to achieve the FOMC's dual mandate of maximum employment and price stability, ensuring a balanced and sustainable economic environment.
The Significance of FOMC Meetings
The FOMC holds eight scheduled meetings annually, during which members review economic and financial conditions and determine appropriate monetary policy actions. These meetings are essential for assessing the state of the economy and making informed decisions regarding interest rates and other policy measures.
The Agenda and Decision-Making Process of FOMC Meetings
During FOMC meetings, members analyze a wide range of economic indicators to inform their decisions. Key topics of discussion include:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Growth: Evaluating the overall health and trajectory of the economy.
- Inflation Rates and Consumer Price Index (CPI): Monitoring price trends to ensure price stability and control inflation.
- Unemployment Levels and Labor Market Conditions: Assessing job creation and workforce participation to support maximum employment.
- Global Economic Developments and Financial Market Trends: Considering international factors that may impact the U.S. economy.
Following thorough deliberation, the FOMC issues a statement summarizing its decisions and offering guidance on future policy actions, providing clarity and direction to stakeholders.
Decoding FOMC Statements
FOMC statements are closely monitored by economists, investors, and policymakers for insights into the committee's decision-making process and future policy intentions. These statements typically include:
- A comprehensive summary of current economic conditions and potential risks.
- A detailed description of the committee's policy actions, such as adjustments to the federal funds rate.
- Forward guidance on the anticipated path of monetary policy.
The Influence of FOMC Statements on Financial Markets
FOMC statements have a profound impact on financial markets, influencing stock prices, bond yields, and currency values. Investors and analysts carefully analyze these statements for clues about future economic conditions and policy changes, using them to inform investment strategies and decision-making processes.
The Broader Impact of FOMC Decisions
The decisions made by the FOMC have far-reaching consequences for the U.S. economy and beyond. By influencing interest rates and credit availability, the committee can stimulate or slow economic growth, manage inflation, and address unemployment challenges.
The Economic Ramifications of FOMC Policies
Key effects of FOMC policies on the economy include:
- Encouraging Consumer Spending and Business Investment: Lower interest rates make borrowing more affordable, boosting consumer spending and business investment.
- Controlling Inflation: Raising interest rates when prices rise too quickly helps manage inflation and maintain price stability.
- Supporting Job Creation and Reducing Unemployment: Accommodative monetary policies can stimulate job growth and reduce unemployment levels.
These effects highlight the critical role of the FOMC in fostering economic stability and promoting sustainable growth.
Investor Perspectives on FOMC Decisions
Investors closely track FOMC decisions and statements to anticipate the future direction of interest rates and economic conditions. Changes in monetary policy can significantly impact asset prices, making it essential for investors to understand the implications of the committee's actions.
Tailoring Investment Strategies to FOMC Decisions
Investors often adjust their strategies in response to FOMC decisions:
- Bond Markets: Rising interest rates typically lead to lower bond prices, while falling rates can increase bond values, influencing fixed-income investments.
- Stock Markets: Accommodative policies often boost equity prices, while tighter policies may lead to market corrections, affecting equity portfolios.
- Currency Markets: Higher interest rates tend to strengthen the U.S. dollar, while lower rates may weaken it, impacting currency-based investments.
By staying informed about FOMC policies, investors can better navigate the complexities of financial markets and optimize their investment strategies.
A Historical Overview of the FOMC
Throughout its history, the FOMC has played a pivotal role in shaping economic policy, addressing challenges such as the Great Depression, inflationary pressures, recessions, and financial crises. The committee's adaptability and commitment to economic stability are evident in its response to evolving economic conditions.
Notable Moments in FOMC History
Key events in FOMC history include:
- The Volcker Era: Under Chairman Paul Volcker, the FOMC implemented stringent monetary policies to combat high inflation during the 1980s, restoring price stability.
- The Great Recession: During the 2008 financial crisis, the FOMC introduced unconventional measures, such as quantitative easing, to stabilize the economy and prevent further collapse.
- Post-Pandemic Recovery: In response to the economic disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, the FOMC implemented aggressive monetary policies to support recovery and address widespread economic challenges.
These historical milestones demonstrate the FOMC's ability to adapt and respond effectively to complex economic challenges.
The Challenges Facing the FOMC Today
Despite its influence, the FOMC encounters numerous challenges in implementing effective monetary policy. These challenges include:
- Global Economic Uncertainties: Navigating geopolitical risks and international economic fluctuations.
- Changing Demographics and Labor Market Dynamics: Addressing shifts in workforce participation and demographic